It is calculated as (Overhead Cost/Prime cost) x 100.Prime cost is nothing but the sum of direct material cost and direct labour cost. Let’s walk through an example of absorption costing to illustrate how it works. Suppose we have a fictional company called XYZ Manufacturing that produces a single product, Widget X. Now, calculate the number of units left in inventory, then multiply by the absorption cost per Accounting Periods and Methods unit. Absorption costing is a managerial accounting method for capturing all the costs related to manufacturing a product.
Overhead Allocation

Absorbed cost allocations for one product produced may be greater or less than another. Absorbed cost, also known as absorption cost, is a concept in managerial accounting where all expenses, both direct and indirect, are built into the overall cost of creating a product. Knowing the full cost of producing each unit enables manufacturers to price their products. Variable overhead costs directly relating to individual cost centers such as supervision and indirect materials.
Allocate costs by type
Under the technique of marginal costing, however, profit remains more or less constant since the same is not affected by variations in stocks. When sales fluctuate but production remains constant, profit increases or decreases with the level of sales whether it is absorption costing or marginal costing, assuming that costs and prices remain constant. However, profit may not be the same under both the techniques due to the existence of stocks and variations in cost per unit during different periods. Outsource Invoicing Under the marginal costing technique, inventories are valued at marginal cost. First of all, Absorption rates are computed for absorption of overheads in costs of the cost units. In an absorption costing system, both the fixed and variable costs are regarded as product related cost.
- Variable costing is more useful than absorption costing if a company wishes to compare different product lines’ potential profitability.
- Effectively applying absorption costing involves several key practices.
- This information helps you monitor your performance more effectively and take action if there are any anomalies in your figures.
- Therefore they have to be distributed to cost centers on some sharing basic like floor areas, machine hours, number of staff, etc.
Top 2 Steps Involved in Absorption Costing (with Formula for calculating Overhead Absorption Rate)
In the case of marginal costing, however, costs are classified on the basis of nature or variability, i.e., fixed and variable costs. Absorption costing refers to the ascertainment of costs after they have been incurred. Here, fixed costs as well as variable costs are allotted to cost units and total overheads are absorbed by actual or normal activity level. Absorption costing is called total, or historical, or traditional, or cost plus costing.

- Under absorption, fixed costs are spread across all units produced, affecting inventory costs.
- It’s important to track your income statement to make sure you don’t exceed your actual costs.
- This is the allocation of the cost of machinery and equipment over their useful life.
- This human effort physically creates the product, including operating machinery, assembling components, and performing tasks essential to production.
- In this method both material cost as well as labour cost is the base for calculating the overhead absorption.
- If you only price based on variable costs, you may not be able to cover your fixed costs.
- In other words, a period cost is not included within the cost of goods sold (COGS) on the income statement.
Companies can use absorption, variable, or throughput costing for internal reports. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and GAAP are primarily concerned with external reporting. The following diagram explains the cost flow for product and period costs. This article will discuss not only the definition of absorption costing, but we will also discuss the formula, calculation, example, advantages, and disadvantages. With the process of primary apportionment or distribution, the loading of overheads for all the departments i.e. production as well as service departments can be obtained. The next step is to transfer the overheads of non-production departments to the production departments, as the various cost centers move through the production departments only.
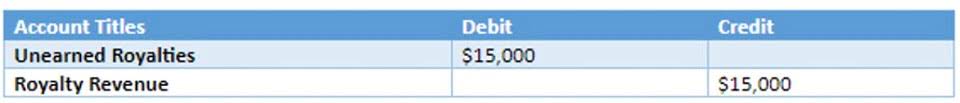

Simplify complex operations with multi-entity management, custom roles and permissions, and automated revenue recognition. Make faster decisions with multi-dimensional reporting and deeper insights in real time. This insight is also valuable input for demand planning, helping align production forecasts with cost structures. This works alongside the revenue recognition principle to ensure income is reported accurately over time.
- Under variable (or marginal) costing, however, only variable costs are treated as product costs.
- There are many who say marginal costing is better, while others prefer absorption costing.
- In the context of absorption costing, the absorption of overhead means that all forms of overhead (both fixed and variable) are included in the final product cost.
- In the case of absorption costing, the profitability or otherwise of a product is influenced by the amount of fixed costs apportioned to it.
- This is because all fixed costs are not deducted from revenues unless all of the company’s manufactured products are sold.
- The next step is to transfer the overheads of non-production departments to the production departments, as the various cost centers move through the production departments only.
External reporting compliance

In case, the business shows seasonal absorption costing formula sales pattern, the production may be built up during the slack season. If so, the operations will show losses during the period of production in the variable costing, and large profits will be shown in the periods when goods are sold. Therefore, the inclusion of fixed costs may, sometimes, lead to improper decisions. As such, absorption costing is of limited significance from the point of view of decision-making. In this system all costs are identified with the manufactured products. Here, the management is interested to know whether a product can generate sufficient return on investment after absorbing its share of costs.